Author’s Thoughts

"AI-powered document comparison is the backbone of today’s plagiarism and paraphrasing detection tools. At Silk Data, we’re focused on creating AI solutions that don’t just spot matching words — they understand the meaning behind the text. This helps us deliver accurate, reliable results you can truly trust."
Nikolai Karelin
AI Document Comparison: A Smarter Way to Understand Semantic Similarity
Text comparison might sound straightforward at first: check if two passages match. But what happens when the wording changes, or when you need to find subtle contradictions in legal documents or ensure due diligence across multiple languages? This is where modern AI, specifically semantic text comparison, takes center stage.
Instead of just matching literal words, today’s AI systems leverage semantic similarity (similarity in meaning, not just matching words) to understand the meaning behind the text. This means they can detect not just identical phrases but also reworded content, semantically related ideas, or subtle shifts in context. Let’s break down how it works.
Real-World Applications of Text Comparison
At its core, text comparison fulfills a simple yet universal need: the ability to find similarities between two texts. Whether you're reviewing contracts or checking for hidden inconsistencies in reports, the ability to analyze text changes has been a game-changer for decades. Here are some key ways text comparison makes a difference in the real world:

Document Version Control
When teams collaborate on reports, proposals, or technical documents, tracking changes is crucial. Imagine working on a business proposal with five different contributors. Some changes are obvious — like added sections — but others are subtle, such as rephrased sentences that could alter the document’s tone or meaning. Text comparison tools highlight these changes instantly, saving hours you'd otherwise spend manually hunting for edits.

Plagiarism Detection
With the rise of AI and paraphrasing tools, plagiarism isn’t just about identical copy-paste issues anymore. Educators, publishers, and content creators need plagiarism tools that go deeper. For instance, a university professor checking a student’s thesis can use text comparison to detect if ideas were lifted from online sources, even if the wording has been cleverly rephrased. This ensures academic integrity beyond surface-level checks.

Legal Document Analysis
Legal teams handle mountains of contracts, policies, and agreements. A minor change—like swapping “shall” for “may”—can have serious legal implications. Text comparison helps lawyers review amendments side by side, quickly spotting contradictions, duplications, or missing clauses. For example, during contract negotiations, a lawyer can compare the latest draft with the original to ensure no critical terms were altered without notice.

Due Diligence in Business and Law
Due diligence often involves analyzing large volumes of documents to identify potential risks or red flags. Picture a merger and acquisition deal where hundreds of contracts need to be reviewed. AI-powered text comparison tools can rapidly detect overlapping clauses, inconsistencies, or even related terms hidden across different documents. This not only saves time but reduces the risk of overlooking crucial details.
The Classical Approach: Lexical Comparison
Early text similarity tools worked by checking if words matched exactly. This method is useful for spotting small changes, such as:
- Fixing typos or punctuation errors.
- Adding or removing individual words.
- Slightly rearranging sentence structure without changing the meaning.
But here’s the problem: this method only looks at words, not semantic relatedness. If a sentence is rewritten with different words but still conveys the same idea, traditional tools won’t recognize it as similar.
For example, the sentences "The weather is nice today" and "It’s a beautiful day outside" have the same meaning, but a word-for-word comparison would see them as completely different.
Older methods simply count word differences without understanding the context. That’s why they fail at detecting paraphrased content—where the words may change, but the meaning stays the same.
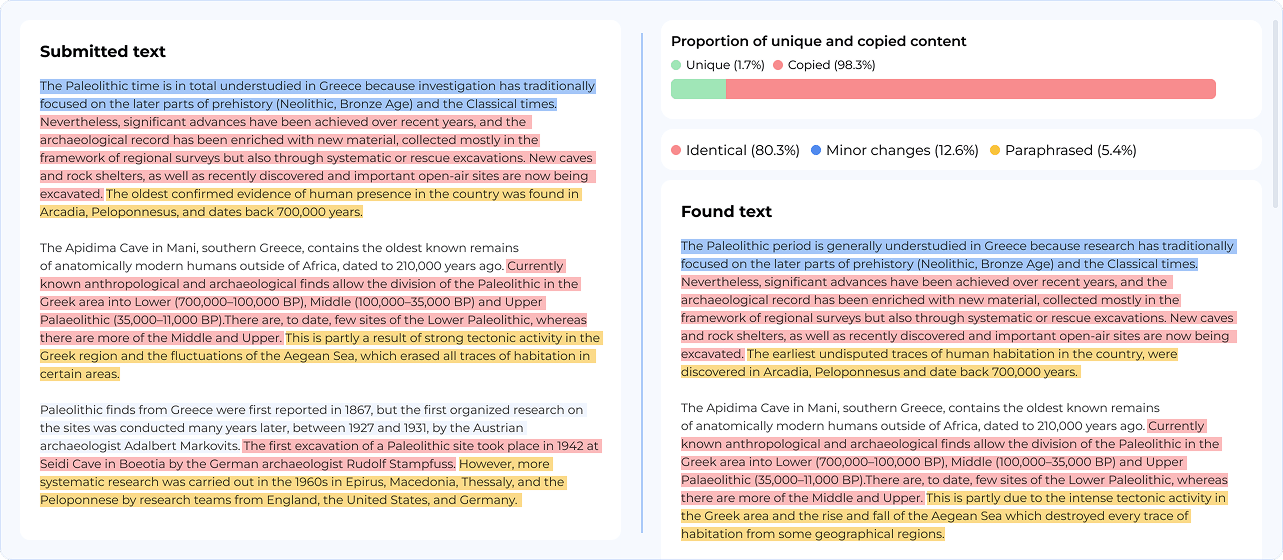
The Rise of Semantic Comparison in Plagiarism Detection
Plagiarism detection was one of the first areas to expose the weaknesses of traditional comparison methods. Verbatim comparisons could only detect copy-pasting, but semantic AI models can detect paraphrased content. For instance:
- Original: "Artificial intelligence is transforming the tech industry".
- Paraphrased: "The technology sector is being revolutionized by AI".
AI comparison tools would flag these sentences as semantically similar.
This capability has made semantic text comparison a must-have tool in marketing, education, publishing, and academia.
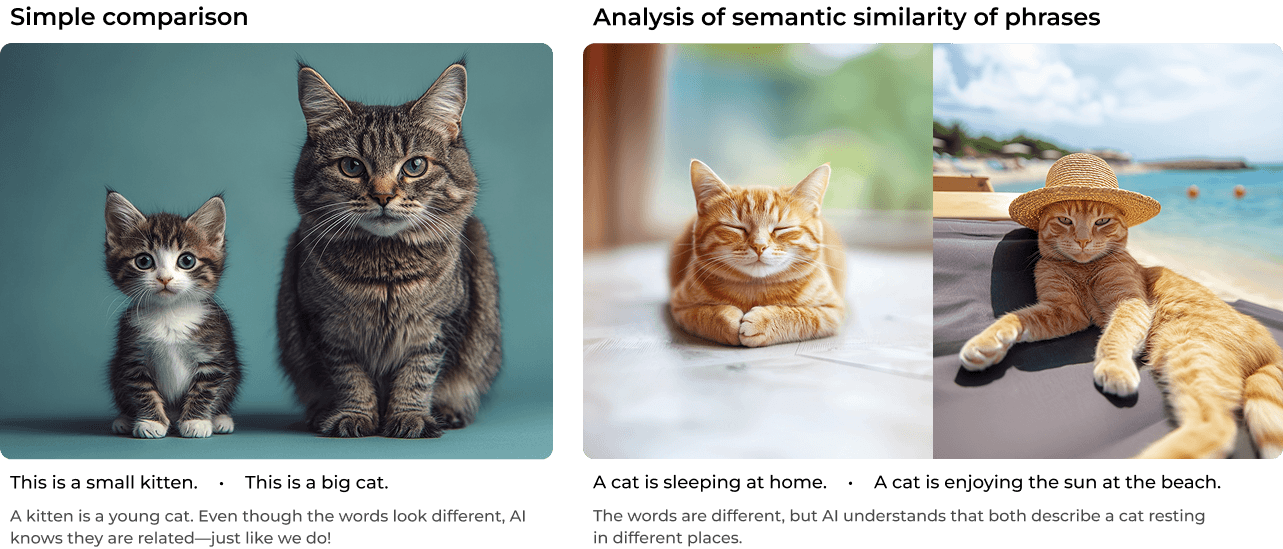
Recent Progress in Language Models
AI has come a long way in understanding and comparing text. Unlike older methods that simply matched words, today’s language models—advanced AI systems trained on massive amounts of text—can understand meaning, context, and relationships between words. And the best part? They can be fine-tuned (optimized) for specific tasks, making them versatile problem-solvers.
Thanks to transformer-based models like BERT, T5, and GPT, AI can now:
Recognize similar ideas, even when phrased differently.
For example, it understands that “The weather is nice today” and “It’s a beautiful day outside” mean the same thing.
Identify logical connections between statements.
AI can determine if one sentence supports, contradicts, or expands on another, which is crucial for summarization and fact-checking.
Classify text by sentiment, topic, or intent.
It can analyze reviews, detect spam, or sort news articles based on subject matter.
Handle multiple languages effortlessly.
AI can compare documents in different languages, making global content analysis and translation much easier.
Improve search results and chatbot responses.
Instead of just matching keywords, AI understands meaning, helping search engines find the most relevant results and making chatbots sound more natural.
Modern AI models don’t just memorize words—they learn patterns, context, and relationships from massive datasets. They can then be fine-tuned for specific tasks, like plagiarism detection, content recommendation, or legal document comparison.
Challenges and Considerations
While AI opens exciting possibilities, there are hurdles to navigate:
Data Security
Sharing sensitive data with cloud-based AI tools may raise privacy concerns. Local (on-premises) solutions can mitigate this but may require more resources.
Hardware Requirements
Running large AI models, especially for training, often needs large number of GPUs and substantial energy demands.
Model and data provenance
There are many powerful open-source models for text processing available today. However, before using one in business, it’s important to review how it was trained, the data it relies on, and the licenses for model, its training data and code used to run the model.
Fine-Tuning Costs
Customizing AI models for specific industries can be time-consuming and require sufficient high-quality data.
Balancing Security and Scalability
Organizations can decide between cloud-based solutions and on-premises systems. While cloud platforms offer scalability and ease of use, they may not meet stringent data privacy regulations in industries like healthcare or finance.
Hardware and Infrastructure
For small projects, regular CPUs are enough to run models. However, large-scale or real-time applications often demand GPU-powered environments. Businesses should weigh the costs of investing in hardware against the benefits of faster, more efficient processing.
Final Words
AI has changed how we compare text. It’s no longer about matching words but about understanding meaning. Whether you’re checking for plagiarism, analyzing contracts or reviewing documents, AI tools provide high accuracy and flexibility. Semantic text comparison is more than just a tool; it’s a bridge to deeper insights, better decisions, and streamlined processes. AI helps organizations use their data better and stay ahead in a complex digital world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Semantic similarity measures how much two texts express the same idea, even if they use different words. For example, “She enjoys reading” and “She loves books” mean the same thing, even though the words are different. AI-powered models analyze context, grammar, and relationships between words to recognize these similarities. This helps in tasks like plagiarism detection, content recommendation, and document comparison.
Text comparison is the process of analyzing two or more pieces of text to find similarities between them. It is widely used for plagiarism detection, document version control, and data analysis. Basic methods compare words directly, while AI-powered tools go further by recognizing synonyms, sentence structures, and even reworded ideas. This allows businesses, researchers, and educators to accurately assess text similarities beyond just exact word matches.
Unlike traditional tools that only detect exact duplicates, AI can recognize paraphrased sentences, translated content, and subtle differences in tone and intent. It’s widely used in automated plagiarism detection, legal document review, content moderation, and multilingual text analysis, making comparisons more precise and insightful.
Lexical similarity compares texts based on exact word matches. It spots typos, punctuation changes, or rearranged sentences but fails to recognize reworded phrases. Semantic similarity, on the other hand, analyzes meaning —understanding that “big” and “large” are the same. AI-based tools use semantic analysis to detect rewritten content, making them much more effective for plagiarism detection, text summarization, and search optimization.
Our Solutions
We work in various directions, providing a vast range of IT and AI services. Moreover, working on any task, we’re able to provide you with products of different complexity and elaboration, including proof of concept, minimum viable product, or full product development.