Expert’s Thoughts

"Mobile development industry appears to be one of the most fast-growing fields of global digital world, being challenged only by AI development. More and more companies are trying to acquire their own mobile application and reach a vast consumer market of mobile users. Still, many of them struggle to dive into mobile development because of the great number of pitfalls.
Silk Data has prepared a comprehensive guide on how to create an app, highlighting the most vital steps that ensure the highest possible quality and business efficiency of your mobile products."
Yuri Svirid, PhD. — CEO Silk Data
Market Insights
For the past years global business has been paying close attention to mobile apps, considering mobile users' market as one of the most promising from the point of business expansion.
The main factors of companies trying to increase their presence there are mentioned in Precedence Research report of April 2025. Here are several insights on global mobile application market:
More than 4 billion mobile devices have been sold in the entire world since 2022.
Mobile application market size reached 330 billion USD by the beginning of 2025 demonstrating annual growth rate of 14,5% . Current estimations are that it will pass the mark of 1 trillion USD in less than 10 years.
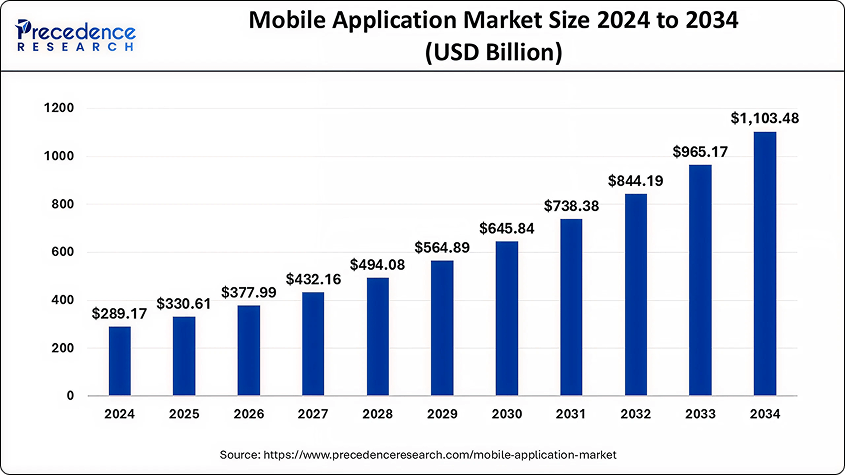
Source: precedenceresearch.com
North America and Asia Pasific regions hold 63% of the global mobile market.
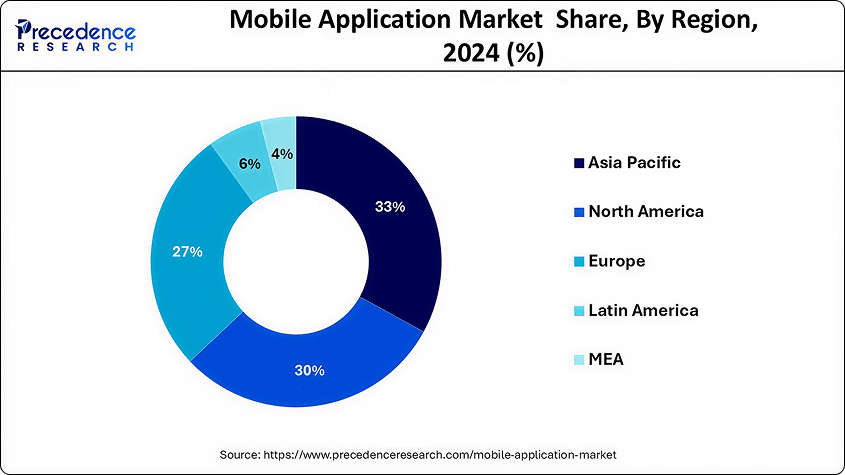
Source: precedenceresearch.com
Main industries represented in mobile apps are Entertainment, Gaming, Health & Fitness, Education & Learning, Retail and E-commerce.
Despite the great perspectives that mobile industry provides for business scaling, companies still face difficulties in developing efficient and attractive mobile applications.
This blogpost provides a step-by-step guide on how to make an app that will attract users and hold more than a month after release.
Key Steps of Mobile Application Development
Working on this guide, we used our comprehensive expertise in creating mobile solutions and implementing AI practices into mobile development . Through that, we not only provide steps, but also share most efficient practices used both by our team and the most outstanding world technological giants.
- 1
Step 1. Define App Idea
The first development step is the most crucial, as it defines functional and operational specification and influences the following steps of mobile app creation.Defining app’s idea, companies should focus on several tasks.
Problems identification
First, you must identify the range of problems your mobile application can work with.
For example, you create a fitness app that monitors the number of steps the user walks per day, calculates the number of calories consumed and burned, periodically reminds about the need for physical activity or can create a full training program.
You can also create a banking app that allows you to process any financial operations (money transfer, online payment, bank account opening and closing) or work on an online store app that promotes convenient shopping in a few clicks.
In other words, this task should be fulfilled to define key app’s functionality and traits that may seem attractive.
Target audience and competitors' research
Next task is to define the ‘ideal customer avatar’, meaning to find the category of potential customers who are most likely to download and interact with your mobile app. You should define the region, age, gender, social standing and professional interests of the people you’d like to promote your product to.
Additionally, your goal is to thoroughly analyze the competitor's market. You should look at the most successful mobile apps in your industry, identify any common traits regarding functionality and design and adopt them.
Note! Working on market research, some companies can lapse into mere copying of the practices used by their more successful competitors. However, such an approach leads to unsatisfactory results, when business loses its uniqueness. You should always look for a balance between creating unique traits and adopting your contenders’ best features.
Idea validation
When the problem identification is finished and TA and competitors research allowed you to come up witha solution, your task now is to prove the solution would work.
The most efficient ways of idea validation are proof-of-concept (POC) and development of minimum viable product (MVP) . POC validates technical and commercial feasibility of an idea, while MVP allows to test stripped-down version of the product with minimal functionality to gather initial feedback from real users.
Both methods allow to clearly see whether an idea is perspective or not.
- 2
Step 2. Choose the Development Approach
Once you have a clear plan on what product you are to develop, the nest step is to choose the right development strategy. Choosing the development approach directly depends on the results of app’s idea validation along with the amount of time and resources you can spend on development.Several options are available.
Native vs Cross-Platform vs Hybrid
First, you can choose between three main mobile development approaches on the criteria of which platform has the highest priority for your business.
1. Native development
A mobile development approach that promotes building apps for one specific platform (iOS or Android) with a usage of platform-specific tools (like Swift and Xcode for iOS and Kotlin for Android). Native app, being optimized for particular OS, demonstrates highest performance while following the platform design guidelines ensures better user experience . At the same time, native mobile development is considered the most expensive and time-consuming.
2. Cross-platform development
An approach that provides a single codebase for both iOS and Android. The ability to be deployed on different platforms provides lower costs and reduced time of development, though the app may lag behind native SDK updates of particular OS. However, cross-platform development solutions are the best option for products requiring UI consistency on any platform (for example, social media or marketplace apps ).
3. Hybrid development
The last approach implies bending web technologies with a native container. The result looks like embedding a website into native app shell . Therefore, hybrid development is the most cost-efficient approach with the lowest time of deployment. At the same time, hybrid apps demonstrate worse performance and limited access to device’s hardware (camera, GPS, etc.).
Here is a clear comparison of all three approaches:
Criteria Native Cross-platform Hybrid Performance Highest Near-native Lowest, WebView dependent Cost of development Highest Medium Lowest Time to market Slowest Medium Fastest UI/UX consistency Follows platform guidelines Customizable but may lack platform nuances Web-like, less native feel Best use cases High-performance apps (games, AR/VR-based, banking apps) Apps needing UI consistency (social media, marketplaces) Simple apps, Internal corporate tools We can also mention one more approach, when the mobile app is developed on native practices but with a possibility to shift to another platform in the future. For example, you can use Jetpack Compose and Compose Multiplatform technologies in Android-based projects to make them available for iOS as well.
No-code and Low-code
If your company lacks technical specialists and doesn’t have enough resources to hire an in-house or outsourced development team, the solution is to apply to no-code or low-code practices.
Both practices imply mobile app building without writing a code or with minimal coding . In doing so, companies can use a great variety of tools, such as Adalo, Bubble, Appgyver, FlutterFlow and many others, for building app’s logic, creating prototypes or generating code for further development.
Despite apparent benefits that allow to build an app in mere days, no-code and low-code has a number of restrictions, like limited customization capabilities and performance trade-offs unsuitable for complicated operations.
If your business wants to create an app that will stand out from competitors through unique approach in user-app interaction and advanced functionality, you can apply to AI mobile development. There are lots of ways AI can help in developing apps, from development cycle optimization to enhanced business’s positioning on the market. Sometimes, it’s even better to implement a ready-to-use solution, based on popular LLM API integration (like ChatGPT) that allows to leverage advanced AI capabilities.
- 3
Step 3. Features Planning and Design
Next crucial step is defining what exact features your app should have and how they should be presented for the user. There’re also a couple of important factors that should be considered.User persona and navigation
Features planning and application design implies defining the goals and possible ways of users interacting with the app. This task is intertwined with the step of idea identification and target audience definition. You define the app idea, look at the most popular applications that followthe same idea and align it with the estimated target audience.
Defining the user persona also helps to create efficient and convenient navigation system. Analyzing the market of potential customers, you notice the pain points and tech habits of the users, so you can focus on proper positioning of blocks, elements and on efficient user navigation.
The main goal is to plan and design the functionality according to the expected behavior of the protentional user, where ease of access, intuitiveness of usage, clear visual cues and consistent user experiences across the app are prioritized.
Wireframes, mockups and prototypes
One more important task necessary for proper features planning and design is the building of the initial prototype. Prototypes visually demonstrate the estimated UX/UI of the application and allow to understand whether they are efficient or not.
The demonstration can be presented through wireframes, mockups or actual app prototypes, and each of them has their own advantages and limitations.
Wireframes are simple sets of images and schematic blocks which display functional elements of the mobile application. They are extremely easy to build and good at initial visualization of ideas, though they lack any details and can't demonstrate how the elements of the app operate.
Mockups are designs that display the color, fonts and positioning of fields and elements. They demonstrate how the mobile app will look for real users on real mobiledevices and help in planning and building the UX and UI parts.
Prototypes are the most complicated type aimed to imitate actions and behavior of the real application. They allow to see how the system reacts to the user’s actions and how the app’s operations work. Though prototypes seem to be the most efficient way of idea, features and design verification, their development takes time, so small companies and startups tend to skip it in order to save limited resources.
Here is a clear comparison of all three types:
Criteria Wireframe Mockup Prototype Best for Early brainstorming, stakeholder alignment Design validation User testing, final UX checks Fidelity Low (schematic) High (pixel-perfect, styled) Interactive (clickable, dynamic) Level of detailing Low (schematic) Includes branding, typography and graphics Mimics real app flow with animations/logic Speed of development Very fast Medium Slow (depends on complexity) Cost of development Low Medium High Limitations No design or functional details presented Non-interactive Time-consuming, excessive for simple ideas Note. A common mistake of prototyping is that teams try to add too many details in their prototypes. According to the dedicated article made by Forbes, users pay most of the attention to no more than 20% of the mobile app’s functions. It means that the main goal of prototyping is to verify efficiency, proper performance, reliability and UX/UI of these prior functions.
We should add one more sufficient note regarding the necessity of textual documentation. Many companies use systems like Wiki and Confluence to record all the important stages and specifications of the project ‘on paper’.
This documentation should be permanently filled with data regarding general project info, architecture, technological stack, API interaction, etc. The main goal of such a documentation is to ensure that the project could be carried on, maintained and updated whenever necessary, so that even the fully new development team could quickly understand the specifics.
Furthermore, such documentation represents a single knowledge base, which can become the basis for further improvements and push project teams for new versions or updates ideas.
- 4
Step 4. Tech Stack Choice and App Developing
Next stage is the development itself that involves three core components: frontend, backend and database development.Frontend
Frontend part defines the outlook and interactivity of the mobile application. The choice of tools used for frontend development directly depends on the development approach you chose on the second stage.
For example, if you decided to achieve the best performance and user experience and applied to native development, you may choose Swift, SwiftUI and UIKit for iOS or Kotlin and Jetpack Compose for Android.
All the tools provide fast, easy and properly controlled frontend development for high-performance products, like mobile games or AI-based apps.
On the other hand, if your choice is to use single codebase within a cross-platform development you can apply to Flutter and React Native frameworks, which were used for development of the most popular mobile apps like Google Pay, Facebook and Instagram .
Overall, frontend development is the part of the development process responsible for a user-facing aspect of mobile applications, like UI elements (buttons, layouts, animations), UX (navigation and responsiveness) along with client-side logic.
Backend
The backend part of mobile app’s development is responsible for proper connection between interface and databases, businessand tech logic, system’s performance, security and scalability.
There’s a great variety of programming languages and tools used for backend development like Java, Kotlin, Go, Python and Node.js , and the right choice depends on the scales of your app and availability of related specialists.
If the resources of your business don’t allow you to hire an in-house development team, you can apply to outsourced development . Silk Data has a lot of experience in IT consulting and outsourcing, and our developers will use all their skills and expertise to provide you with the most efficient solution.
DatabaseMobile app’s database development is the task for data architects and developers who are responsible for system’s data organization, optimization along with ensuring database’s security and scalability.
It also refers to the operations required withinthe mobile app, like queries processing and data transactions.
The tech stack depends on the type of database and can be presented by MySQL and PostgreSQL for relational databases (with strictly structured data, for example, user profiles data) or Mongo DB for databases that contain flexible and unstructured data.
- 5
Step 5. App Testing
The final stage of mobile app development refers to the testing of the final product.Note! The application’s testing is a process that goes alongside all the other development stages from idea verification to final pre-release stages. We have thoroughly discovered the essence of software and application testing in one of our previous blogposts and highlighted the importance of permanent product quality control.
The large process of application testing is typically divided into three main sections: functional, non-functional and specified testing.
Functional
The main purpose of functional testing lies in validation of mobile app’s functions’ compliance with initial requirements. The functional testing is also divided into sub-types, each of them responsible for a particular aspect of mobile app’s performance.
For example, unit testing allows to test separated app’s components like menus, lists, buttons, fields and their reaction to user’s actions. At the same time, system testing allows to see whether all the components properly work together as a system.
Non-functional
The second aspect of mobile app’s testing is responsible for approving and ensuring its security, scalability, and high-performance capabilities along with application’s convenience for users.
Testing of the above-mentioned aspects is carried out by imitation of user traffic or cyber-attacks, putting the system in non-standard conditionor checking its performance on different OS and mobile devices.
Specified testing
Specified testing refers to the specific cases where functional and non-functional types are not enough.
For example, if your product is an AI-based mobile application , you’ll need AI and ML testing practices based on the usage of special tools, like TensorFlow and MLFlow. Altogether, they’ll ensure AI model’s logic, detect its vulnerabilities and identify periods of downfalls.
- 6
Step 6. Deployment and Post-Launch Maintenance
Finally, the process comes to the app’s deployment and launch on AppStore, Google Play or both. However, the work doesn’t end here. Now, it’s time for permanent support for your product which includes lots of tasks regarding technical and commercial maintenance.System monitoring
One of the main tasks for you as for mobile app owner is to closely look after the work of your product.
A dedicated team of specialists should monitor its performance and track bugs, downfalls and other issues that can negatively affect the user experience and satisfaction. In addition, any mobile project should have ‘crushes’ library, where all the data about app’s downfalls and performance problems are gathered.
The best way is to use the capabilities of AI-based predictive analytics that will notify about the possible problems and their outcomes by analyzing historical data regarding the app’s work.
Feedback gathering
In order to quickly track the problems and see the directions of the mobile app’s further improvements, you should pay close attention to the user’s feedback.
The customers reviews are a good source of information about the problems which can occur while interacting with an app and which were neglected while its testing.
Moreover, users can leave feedback regarding the desirable features which can become the basis for further mobile application updates.
Updating
Next task is to plan regular updates of your mobile app. According to Statista, 95% of apps on Google Play are updated yearly .
The release of new versions is crucial for the product’s quality maintenance andimprovement, as updates imply bug fixes and new features added.
What is more crucial is the fact that annual updates are necessary even just to ensure that applications support the latest OS versions. For instance, Google Play may delete apps that do not support new versions of Android from their apps catalogue .
However, you don’t have to seek frequent updates, as it can lead to additional problems when the new versions’ quality has been sacrificed for speed.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in App Development

Excessive Interface and Functionality
A common mistake in mobile app development is creating an interface with too many elements or packing the app with excessive features.
Overly complex interfaces overwhelm users, making navigation difficult and the overall experience frustrating. The Statista research dedicated to user experience says that 52% of mobile users find convenience and aesthetics as prior reasons for abandoning the app .
Additionally, implementing too many features into an app can lead to performance issues, slower load times, and higher battery consumption .
In other words, minimalist design with intuitive navigation and carefully selected features typically results in better user retention and satisfaction.

Ignoring Personalization
Many apps fail to incorporate personalization, treating all users identically regardless of their preferences or behavior. Such an approach misses opportunities to enhance engagement and build loyalty. That’s why development and marketing teams work in close cooperation and use tools like Firebase Analytics to understand how users interact with the mobile application.
The vast research made by Salesforce in 2023, says that 60% of users place an emphasis on increased personalization and individual attention, while 8 of 10 customers want to be considered as individuals, not just another number in the sales statistics.
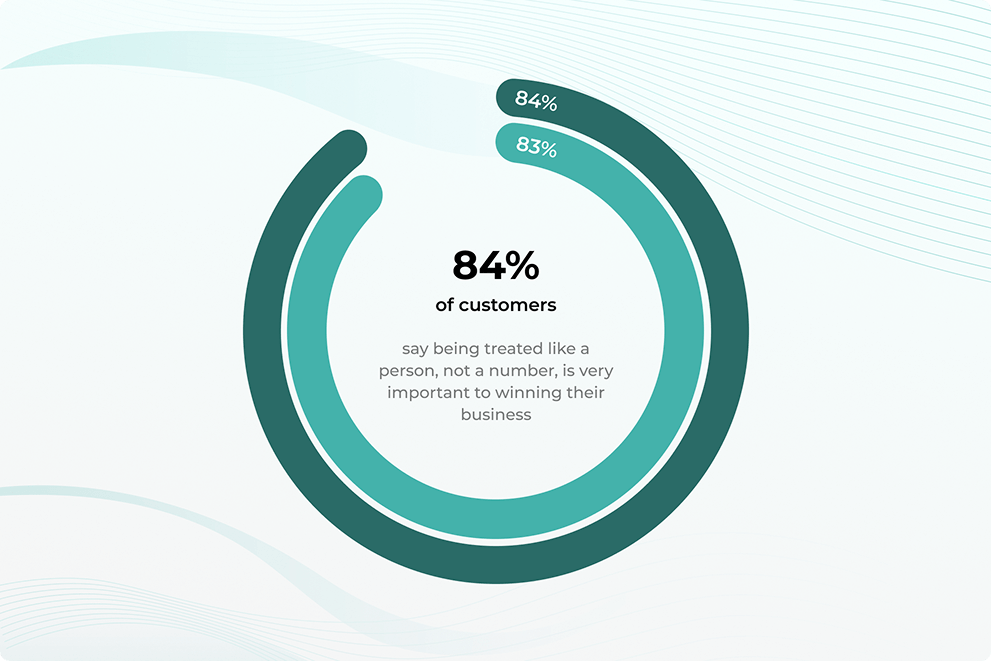
Users today expect experiences tailored to their needs, whether through customized content, adaptive interfaces, or personalized recommendations. Without these elements, an app can feel generic and impersonal, leading to lower user retention.
Implementing basic personalization features, such as user-specific dashboards, behavior-based suggestions, or adjustable settings, can significantly improve the user experience and make the app more competitive in a market.
Moreover, there are lots of tools that allow to customize the app’s UI remotely, without the whole application updating. For example, Firebase Remote Config – a cloud service offered by Google's Firebase platform that allows developers to change the behavior and appearance of their app in real-time without requiring users to download an update.
For example, if you are at the brink of Christmas, Easter or any other large occasion, you can apply any thematic holiday interface, while the user doesn’t have to update the application to see it.

Skipping Beta Testing
Launching an app without thorough beta testing is a risky move that often leads to avoidable problems. Beta testing provides critical insights into real-world usage, uncovering bugs, performance issues, and usability flaws that might not appear during internal testing. Skipping this phase can result in negative reviews, high uninstall rates, and damage to the app's reputation.
A well-structured beta test involves releasing the app to a controlled group of users, collecting feedback, and addressing issues before the official launch. This step ensures a smoother rollout and a more polished final product.
Testing itself is an important part of the mobile development process. For example, Google Play provides internal, closed and open testing capabilities for mobile apps.
Internal testing is the testing of a large group of internal testers (up to 100 specialists). Closed testing may be available to a larger number, but invitations for testing are still sent out manually, and the testers can be specifically chosen according to custom criteria. At the sametime, the open testing process can be joined by anyone.
All three approaches ensure the product’s value from different aspects and provide multi-stage quality verification. Our experience says that the best way of mobile application testing is in the following sequence: corporate manual and automation tests (Unit, UI tests, etc.) -> internal testing -> closed testing -> open testing.

Neglecting Maintenance and Optimization
Some developers treat the app launch as the final milestone, neglecting ongoing maintenance and optimization. However, your app requires continuous updates to remain functional, secure and competitive.
Without maintenance, performance can degrade, bugs can accumulate, and security vulnerabilities may emerge. Additionally, failing to optimize the app over time means missing opportunities to improve speed, reduce resource usage, and enhance features based on user feedback. A successful app is never truly "finished"— it evolves through consistent updates and refinements.
Conclusion
The mobile app market continues to expand at an unprecedented rate, offering immense opportunities for businesses willing to invest in high-quality digital solutions. However, as this guide has shown, creating a successful app requires careful planning, strategic decision-making, and continuous refinement.
From defining a clear app idea and choosing the right development approach to designing an intuitive user experience and rigorously testing functionality — each step plays a crucial role in ensuring your app stands out in a competitive market. Avoiding common pitfalls like feature overload, lack of personalization, and inadequate testing can make the difference between an app that thrives and one that fades into obscurity.
If you're ready to turn your app vision into reality but need expert guidance, Silk Data is here to help. Our team specializes in end-to-end mobile development, combining technical expertise with industry insights to deliver solutions that drive engagement and growth.
Our Solutions
We work in various directions, providing a vast range of IT and AI services. Moreover, working on any task, we’re able to provide you with products of different complexity and elaboration, including proof of concept, minimum viable product, or full product development.