Expert’s Thoughts

"The mobile industry remains one of the most fast-growing with new trends and tendencies appearing every year. One of these tendencies is the spread of payment apps.
First received a significant boost during the Covid-19 pandemic, they demonstrate the same increase of adoption in 2025.
Silk Data has prepared this blogpost to highlight the key insights of mobile payment industry and share their knowledge on how to create applications of such a kind."
Yuri Svirid, PhD. — CEO Silk Data
Market Insights
Sensor Tower has prepared a comprehensive report named ‘State of Mobile 2025’ , and the part dedicated to finance applications provides the following insights:
- Finance app downloads exceeded 7 billion in 2024.
- The combined time spent on finance apps exceeded 21 billion hours.
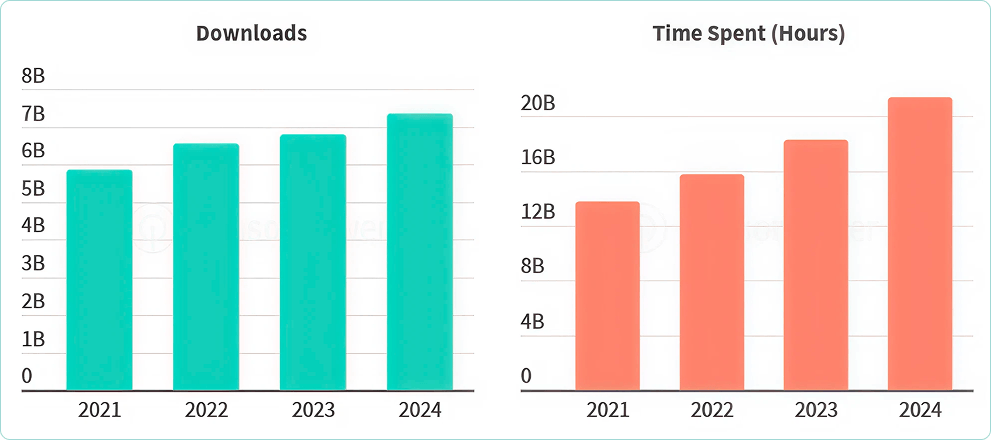
Source: https://dataai.infogram.com/1pw0pyxgqj12j5av7n39evd39nt9ep6zppy
- The top three payment apps on the number of downloads are Phone Pe, Google Pay and PayPal.
In addition, according to Business Research Company report, in 2025 the mobile payment market size reached 107 billion USD with an annual growth rate of 30%. This number means that the market size will triple in less than 5 years.
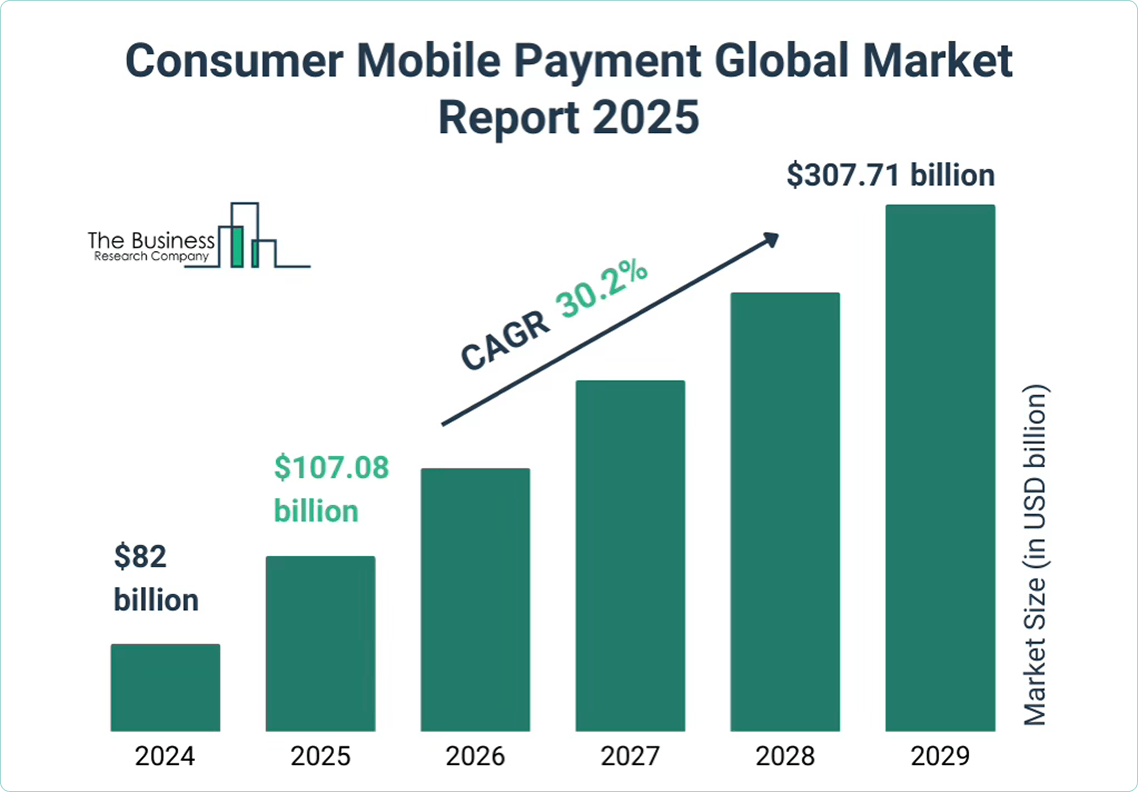
Source: https://www.thebusinessresearchcompany.com/report/consumer-mobile-payment-global-market-report
The above-mentioned data demands business’s close attention to the industry. Through that, Silk Data presents the following blogpost as an overview on the essence of mobile payment applications and the process of their development.
What are Payment Apps and How do They Work?
First, let’s dive into the essence and working principles of mobile payment apps.
These are mobile applications which main purpose is to facilitate financial operations (money, sending and receiving, purchasing, funds management) via mobile devices.
Considered as some sort of novelty several years ago, mobile payment apps have quickly become familiar. In 2022 Pew Research Center prepared a report about payment apps security concerns and one of the facts was that only in the United States 76% of adults had ever used at least one mobile payment application.
At their core, these mobile applications perform the role of intermediaries between financial institutions, customers and goods and services providers.
The process of mobile payment is very simple from its outlook but rather complicated from the technical part.
- User authentication and authorization. To process the payment, the application will require the user’s identity verification. In most cases it’s performed via biometric data verification (fingerprint, Face ID) or PIN entering.
- Transaction system communication. Next step is the mobile app preparing to interact with vendor’s or service provider’s transaction system. It can be processed via NFC (near-field communication) when you tap or just hover on a mobile device near the terminal or via QR code scanning.
It is worth mentioning that within the context of Google Pay usage, the above-mentioned points can be skipped. Google Pay API already provides ready-to-use security infrastructure that doesn’t require the implementation of separate security features, as it uses biometric data or passwords of Android devices.
- Transaction request. Once your mobile device and the one of vendor’s started their interaction, your financial institute (a bank) receives a transaction request, which includes details regarding the amount of money to be paid and the good provider’s info and identity.
- Transaction approval/decline. Next step is when your bank checks the transaction info for possible fraud and other dangerous issues and matches the required sum with the sum on your account. If there’re no dangerous concerns, they send an approval or decline the operation, if any problems are detected.
- Transaction confirmation. The last step is when a service provider or vendor sees the information about the transaction result via their own system update.
In essence, the whole process can take no more than 30 seconds (in most cases 5-10 seconds), except for the cases of poor Internet connection or issues regarding the work of financial institutes.
The most crucial part of the process is how the user data is preserved from leaking or theft.
The first technology is tokenization. This is a security process that replaces vital user data (credit card details or bank account data) with random values called tokens. Tokens ‘cover’ your real data during transactions, while tokenization is a common practice used by all large card networks, including Visa and Mastercard.
The second technology is encryption – a process that turns readable data into an unreadable cluster of elements called ciphertext.
To get the data into its original form or decrypt it, the party should have a special ‘key’. It means that the covering given by encryption is reversable, while tokenization replaces the data entirely.
Silk Data has mastered the usage of the above-mentioned techniques, providing enhanced security in transactions. Moreover, our expertise reaches beyond the development of mobile applications, as we have created a contactless payment solution for transactions via watches along with a mobile payment app that provides connection between user’s bank account and wearables (like digital bracelets or rings).
Types of Mobile Payment Apps
Traditionally, mobile apps for payment are divided into three large groups, and each of them has its own advantages and inconveniences for both customers and business.

Closed-loop apps
The first type are apps that operate only within a restricted transaction network and can only be used within a particular commercial chain.
For example, Starbucks promotes their own free Starbucks App available for both Android and iOS devices. It allows to make orders ahead, search for coffee shops near the user’s location and serves as one of the sources of the company’s marketing strategy. In addition, users can pay for purchases using the application with internal payment points.
Though closed-loop apps provide minimized transaction fees and offer various gifts and discounts, the user remains ‘trapped’ within the app.
There’s no possibility to use such apps outside the commercial network system, and no bank or card operations are possible. It means that the user can’t transfer any money outside the system.
In other words, apps of this kind are meant to be used only in specific stores, being a part of the business’s strategy of enhancing customer loyalty and attracting new clients.

Open-loop apps
The second category is open-loop apps with the largest number of representatives in the industry.
These are the apps connected to global financial networks and accepted by most commercial organizations and stores around the world.
Open-loop apps are typically connected to the user’s real banking accounts or credit and debit cards and can work anywhere the payment network (like Visa or Mastercard) is accepted.
The most famous examples of open-loop apps are Apple Pay, Google Pay and Samsung Pay, as well as payment applications developed and promoted by some of the banks or global and local payment networks.
To conclude, this type of payment app provides the best checkout customer experience, though it rarely has any special offerings and implies higher transaction fees for businesses.

Peer-to-peer payment apps
The third type is peer-to-peer or P2P payment applications.
The main factor that differs this type from the other two is that P2P apps are typically used for person-to-person transfers with a very limited usage area in merchant networks.
The most prominent example of P2P app is PayPal which is considered the third largest mobile payment solution in the world after Apple Pay and Google Pay with 430 million people and organizations using it and more than 26 billion transactions processed (considering its affiliated services, like Venmo) in 2024 only (Business of Apps Report).
Apps like PayPal provide direct transfers between individuals and don’t require any cash or card details for creating an account. However, you still need a real bank account to top up the balance and far from all the companies or small stores will accept payment via P2P applications.
Nevertheless, these mobile payment apps are most commonly used for online purchases or digital products acquisition.
The comparison of all three types is provided at the following table:
| Criteria | Closed-loop apps | Open-loop apps | Peer-to-peer apps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Usage area | Single merchant/commercial chain | Anywhere cards accepted | Person-to-person and online purchases |
| Funding and top up | Preloaded balance | Linked bank/card | Bank transfer or in-app balance |
| Interoperability | None (closed system) | High (works globally) | Medium (requires app adoption) |
| Famous examples | Starbucks App, Amazon Pay | Apple Pay, Google Pay | PayPal, Venmo |
How to Create a Mobile Payment App?
In most cases, businesses that plan to acquire their own mobile payment application stop at the closed-loop app option, as it requires far less concerns on financial regulations, provides minimal transaction fees and can be a good tool in company’s promotion.
The development of such an application like any mobile app development involves a series of carefully planned steps. These are the main ones.

Goal setting
The process begins with goal setting. It is a stage where you must clearly define the purpose of your app, identify your target audience and understand what makes your solution unique in the competitive market.
It can be just a simple app which provides only payment capabilities, or you can also promote loyalty programs and special offers to your customers. The goal setting stage certainly defines all the following stages.

Functionality planning
Once the vision is established, functionality planning becomes crucial. This stage involves determining the core features of your payment app. These features typically include:
- User registration and identity verification.
- Fund transfer functionality.
- Payment processing.
- Bank cards linking and relinking.
- Transaction history.
- Payment analytics.
- Personal data security measures.
It is worth noticing that the number of key functions can differ and directly depend on the goal you set for your mobile application.

System architecting
System architecting forms the technical foundation of your payment app. This involves designing a backend infrastructure tailored for secure transactions processing, selecting appropriate database solutions for storing sensitive financial data and integrating it with payment processors.

UX/UI building
The UX/UI building phase transforms your technical plans into an intuitive user experience. Designers can create wireframes or even prototypes that map user flows for key financial operations like sending money or checking balances.
There are a great number of design techniques, tools and methods used in mobile applications UX/UI building. Nevertheless, there’ s a common rule that the interface should prioritize simplicity and security, with clear visual cues for financial actions and safeguards against errors. At the same time, accessibility considerations ensure the app can be used by people with varying levels of technical literacy and physical abilities on different devices and OSs.

App developing
Actual app development brings all the previous stages together through technical implementation. Developers implement the frontend interfaces for iOS or Android (or both) platforms while building the backend systems that process transactions and manage user accounts.
This stage requires particular attention to security implementations like encryption protocols and authentication methods that were mentioned in the previous part of the blogpost.
The development stage also implies choice of the right approach whether it would be native or cross-platform application, which means specific technological stack (like Swift and Xcode for iOS, Kotlin for Android and React Native, Flutter, and Xamarin for cross-platform). The same applies to low-code and no-code development practices where tools like Adalo, Bubble and FlutterFlow are used in building app’s logic, creating prototypes or generating code templates.
We have thoroughly discovered the above-mentioned process in our previous blogpost dedicated to proper mobile application development, highlighting different approaches of functionality, architecture and design planning along with various tools and technologies used in application development.

Quality assurance and post-release maintenance
Quality assurance represents a critical stage before launching. Security specialists conduct penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities, while performance tests verify the app can handle peak transaction volumes. Real-world usability testing with representative users provides valuable feedback on the app's intuitiveness and reliability. Compliance audits ensure that all financial regulations are properly implemented.
It is necessary to remember that all the above-mentioned operations and testing practices should be performed simultaneously with all the other stages during the whole development process. Testing of the goals and requirements you set is no less crucial than the final pre-release check.
At the same time, the release and maintenance phases mark the transition from development to operation.
Post-release ongoing maintenance addresses technical and security issues, implements security updates, and adds new features based on user feedback and market trends. Continuous monitoring of transaction patterns helps detect and prevent fraudulent activity while providing insights for future improvements.
Conclusion
As evidenced by market data, finance app downloads and usage hours have reached unprecedented levels, with projections indicating sustained expansion in the coming years. Businesses looking to capitalize on this trend must carefully consider their approach to payment app development — whether opting for closed-loop solutions to enhance customer loyalty, open-loop systems for broader interoperability or P2P platforms for seamless peer transactions.
Successful payment app development hinges on a structured process: from defining clear objectives and planning core functionalities to implementing robust security measures and ensuring further product maintenance.
At Silk Data, we combine technical expertise with industry insights to deliver secure, scalable payment solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you're developing a merchant-specific app or integrating wearables for contactless payments, our team ensures cutting-edge technology aligns with your strategic goals.
Our Solutions
We work in various directions, providing a vast range of IT and AI services. Moreover, working on any task, we’re able to provide you with products of different complexity and elaboration, including proof of concept, minimum viable product, or full product development.