Expert’s Thoughts

"The global consumer market demonstrates greater demand for high-quality products. According to Zendesk statistics of February 2025, over 50% of consumers will choose competitors after a single unsatisfactory experience with your product. Through that, companies have to pay more attention to their products’ testing in both web and mobile development. The following blogpost provides a comprehensive overview on types of testing and testing levels and provides understanding on how they help to ensure product’s quality."
Yuri Svirid, PhD. — CEO Silk Data
Market Insights
Software testing has become an integral part of business processes, crucial for assuring the company’s success on the market.
By 2025, the industry demonstrates the following condition rates:
Software testing industry market size has achieved 59 billion USD with annual growth rate of 7%, which means that the market size will achieve 100 billion USD by the end of 2032 ( Global Market Insights ).
North America occupies 42% of the global software testing market (Research Nester).
The industries that demonstrate the greatest need in testing are Healthcare, Finances, Transport, Retail and Manufacturing . The main reason for that is the rapid adoption of new technologies and increased necessity to enhance productivity (Research Nester) .
The increasing demand for the highest possible quality of digital products and greater scales of new technologies acceptance caused the situation when software testing occupied a new role. It’s no longer a tool for mere development support or a mean of tracking errors - it’s a complicated system implemented into the entire development, deployment and delivery cycle .
Through that, testing has become a complex entity with various types and structured hierarchy, where each element or category is responsible for a particular field.
Silk Data presents this blogpost to consider different testing types, examine the levels of software testing and mark the common errors that often lead to downfalls of digital products’ quality.
Main Software Testing Types
There are many criteria on which we can categorize testing, and in the following overview we’ll differ testing types by purpose, technique and level of execution.

Functional Testing
The first type that covers the large field of software testing is functional testing. Its main purpose is to validate whether digital products (software, app, website) function in compliance with requirements.
In other words, functional testing is responsible for correct performance of software’s functions, therefore it is considered as the prior testing type.
Traditionally, functional testing is divided into sub-types. The most crucial of them are unit testing (testing of isolated individual product components), integration testing (verifying proper interaction between modules), system testing (testing of the entire system) and acceptance testing (proving that the product is ready for production). Each of them refers to testing leveling that will be discovered further.
Except the above-mentioned sub-types, functional testing also includes regression testing and API testing, while each of them is the most suitable for particular product parts and stages of development.
For instance, smoke testing as a functional testing practice, is good for cases when you need to quickly check the working capacity of critical functions, while regression testing is used for verifying quality after any changes made in product’s functionality.

Non-functional Testing
Second software testing type primarily focuses on aspects that lie beyond the correct work of product’s functions and modules. The main purpose is to check performance, security, usability and compatibility of the system.
Through that, non-functional testing is also divided into several sub-types.
Performance Testing
A non-functional testing sub-type primarily responsible for checking systems behavior in various conditions. It includes:
- Load testing. The testing system’s performance in the conditions of normal expected load, its performance and stability during the long working sessions.
- Stress testing. Puts the system in excessive workloads to see the limits of its performance capabilities and find the point when it crumbles along with its behavior while restoring.
- Scalability testing. A software testing sub-type that allows to see the system performance in dynamic by gradually increasing workload. It helps to understand whether the bottlenecks could be fixed through system’s scaling or not.
Security Testing
A sub-type of non-functional testing that checks the level of system’s protection from both external and internal failures.
In most cases, the system’s security is challenged through penetration testing (when testers imitate cyber-attacks) and vulnerability testing (when testers scan the system for any security flaws and weaknesses).
Usability and Compatibility Testing
One more sub-type that ensures a product’s usability (i.e. how simple and effective the product is from the users’ point of view) and compatibility (how the product works on different devices, operational systems, etc.).
The sub-type is crucial for cross-platform products or websites to achieve, as it helps to achieve user experience, convenience and satisfaction enhancement .

Maintenance Testing
The type of software testing that is traditionally processed after the product deployment and production.
The goal of maintenance testing is to ensure product’s stability and smooth uninterrupted work.
The main practices of performing maintenance testing are immediate testing after updates (regression testing) or ensuring the results of previous bug fixes (patch testing and validation) . In addition, maintenance testing is also necessary while software versions updating (so the compatibility checking is performed), migrating to a new server, updating OS versions (both server and client) and databases along with changing APIs of third-party services.

Specialized Testing Types
The last category of software testing unites testing practices and techniques regarding specific cases.
For example, AI and ML testing is a testing practice that focuses on machine learning and AI solutions accuracy and performance validation. In doing so, testers use special tools like TensorFlow and MLFlow, which allow to efficiently check AI systems for vulnerabilities and bottlenecks and validate AI model logic.
Four Main Testing Levels
The product’s quality is assured through consistent and efficient testing, where all aspects are considered. Through that, 4 key levels of testing exist. Their hierarchy is presented on the following primitive scheme.
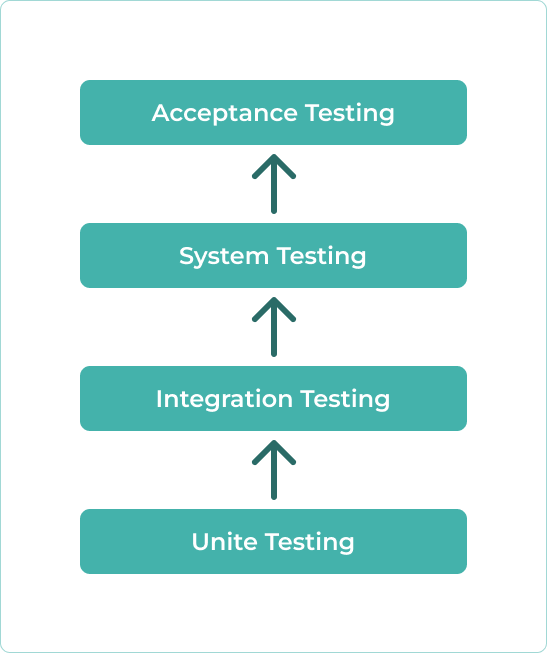

Unit Testing
The first level focuses on testing individual system components, functions or methods in isolation. The main goal is to verify whether these components align with functional requirements and function properly.
For example, QA specialists can check how app’s login function reacts to invalid data or verify the availability of goods in the online store cart when adding them. It’s worth mentioning though that unit tests are primarily the responsibility of developers, who write these tests along with the code.
Automated unit testing can be performed through a number of tools (the choice depends on the ecosystem you work with) like JUnit (for Java), Pytest (for Python) or NUnit (for C#) that can automatically run hundreds of tests in mere seconds, while Mockito and Unittest.moc can simulate system dependences (like databases and APIs) for isolated testing of system units.

Integration Testing
Next level is responsible for verification of proper interaction between modules. For example, QA engineers check correct integration between the above-mentioned online store shopping cart and payment getaway.
In doing so, testers also rely on a number of special tools like Postman (for API testing) and Selenium (for UI integration).

System Testing
The third level of software testing focuses on end-to-end checks of the entire system and its compliance with initial requirements along with the testing system’s performance.
For example, tools like SoapUI or Load Runner allow to simulate multiple users' activity to check website or app performance.
At this stage, QA testers can find problems that were not detected at the previous levels, so any fixes can be made before the system is presented to real users.

Acceptance Testing
The final level of software testing is responsible for assuring the product’s readiness for final production. The main goal is to get both business and user approval.
For this purpose, development companies launch beta testing campaigns , where a limited number of users are allowed to interact with the product.
As an example, a newly developed CRM system can be provided to the client before final production. At the same time, beta testing is a common practice in the gaming industry, when a limited number of players can play the game before its official release.
Through that, companies get informative feedback on the product’s real condition and get a firm basis for additional testing and bug fixing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Software Testing
Despite the great variety of testing sub-types, techniques and tools, companies still make mistakes trying to speed up the product development cycle and reduce costs. As a result, it leads to a sufficient quality downfall and a decrease in user satisfaction.
There are several famous cases regarding business’s suffering from poor testing.
- Y2K or Year 2000 problem. The term used for description of both an event and a technical problem regarding the potential computer errors related to the formatting and storage of calendar data for dates. Computer systems' inability to distinguish dates correctly (like 1900 and 2000) brought down worldwide infrastructures for computer-reliant industries. As a result, around 450 billion USD was spent on preventive operations (software upgrades, testing and consulting), while many organizations worldwide lost 10-20 billion USD in total because of outages.
- Lion Air Flight 610 crash of 2018. The deadliest accident involving the Boeing 737 family, claiming the lives of 181 passengers and 8 crew members. Further investigation revealed that a new software function in the flight control system caused the aircraft to nose down , while the software-dedicated info was removed from aircraft documentation.
- CrowdStrike-related IT outages of 2024. Falcon Sensor security software caused widespread problems with Microsoft Windows computers running the software, because of the faulty update distribution. As a result, roughly 8.5 million systems crashed and were unable to properly restart.
Even without considering the above-mentioned tragic cases, companies still neglect lots of testing practices or make mistakes regarding quality assurance. Here are the most widespread mistakes made by companies.

Neglecting Test Plan Creation
In essence, the first thing that should be done before a new feature or product development and before the testing itself is the creation of a test plan.
It is a document aimed at describing the process of the upcoming testing, highlighting all its key criteria, aspects and specifics.
Traditionally, test plan document includes the following key points:
- Introduction. Brief overview of the test plan, objectives and testing scope.
- Test items. List of components, features and functions to be tested (usually followed by design and requirements documentation references).
- Test approach. Description of the planned testing strategy (whether manual or automated testing is required), testing types (functional, performance, security, etc.) and testing levels (unit, integration, system, etc.).
- Test pass/fail criteria. Define whether the test is passed or failed.
- List of test deliverables. Includes the list of documents that should be produced while testing ( checklists, test cases, reports, etc.).
- Responsibilities. Defining who is responsible for different aspects of testing (test planning, test case development, defect management, reporting, etc.).
- Schedule and Milestones. Includes test activities, timelines and deadlines along with different milestones (for example, test execution start/end).
- Risks and Contingencies. Describes possible risks, delays, resource shortages and possible ways of mitigation.
Test plan is one of the most crucial parts of software testing as it allows to clearly define all the tasks to be performed along with the necessary tools, expected timelines, potential risks and planned responsibilities division in the following testing process.
In addition, the test plan indicates the criteria of entry and exit (i.e., defining the points where the testing should start and end).
Through that, neglecting the test plan documents creation may save time in a short perspective, but in the future, it leads to sufficient delays of product testing and deployment and unnecessary complications in the work of developers and QA engineers. The reasons for that are undefined requirements and responsibilities, unclear deadlines and no fixed criteria for testing entry and exit.

Skipping Unit Tests for 'speed'
Businesses prefer to start with integration or system testing, completely ignoring the first level. Though it may seem like a good time-saver, in reality it leads to a greater number of problems in further perspective.
According to IBM Systems Science Institute, 70% of system bugs are detected within a unit testing level. Skipping the level quickly leads to a so-called ‘technical debt accumulation’ when unidentified bugs scale and cause more and more problems. As a result, saving time at early stages, companies get stuck when the product is close to production.

Ignoring Non-functional Testing
Many businesses also consider functional testing as the most vital testing type, paying minimal attention to other aspects.
However, non-functional testing sub-types, like performance or usability testing play a crucial role in final product’s quality. System’s performance and convenience are crucial for positive user experience, and their neglection leads to decreased interest in product.

Avoiding Early Testing
Some businesses also don’t pay enough attention to testing at the early stages of a project, delaying it until the end of development.
The main disadvantage of the following approach is that defects can accumulate and bug fixing becomes more complicated.
That’s why testing should be performed as early as possible, from the stage of requirements preparation. A good solution for that, that also allows to avoid extra time and money spendings, is integrating testing into CI/CD pipelines and automation of repetitive testing tasks.
Indeed, the best option is to start testing before any coding starts, as the testing of product technical requirements is no less vital than the testing of ready-to-use functions. However, if the product is ready for release, but the QA was inadequate, Silk Data is ready to test your final product and even prepare and implement auto tests into the already released product to simplify the process of adding new features.
A Few More Words about Automation Testing
For the past years, the software testing market has observed rapid growth in automation practices. Here are some insights on the automation testing condition in 2024-2025.
- 51% of testers worldwide reduced at least 50% of manual testing efforts thanks to automation practices. ( PractiTest State of Testing report of 2024 )
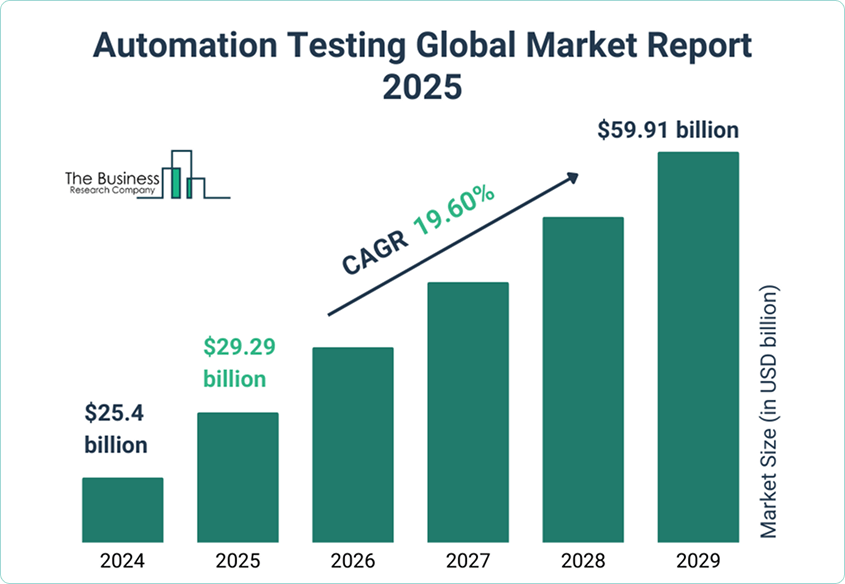
- At the beginning of 2025 the size of automation testing market was estimated at almost 30 billion USD, and, with the annual growth rate of 20%, the number will double by 2029 ( Business Research Company ).
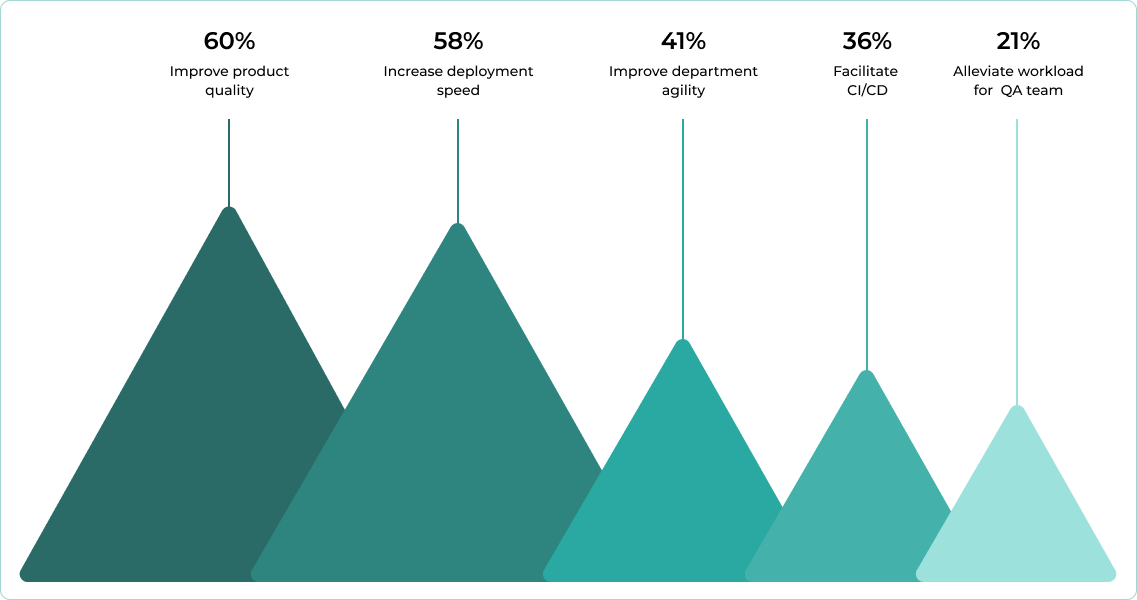
In 2024 the main reasons why companies applied to automation testing were product quality improvement, increase in deployment speed, improved departmental agility and QA teams workload optimization (Gartner) .
Indeed, automation provides sufficient aid in software testing, significantly optimizing the work of QA teams (for example, the time spent on regression testing can be decreased ten-fold compared to manual practices).
The weak spot of automation testing is in the fact that the saved time should be partially spent on creation and maintenance of these auto tests. In many cases it repels the business from auto testing, as at the first stages the process goes slower than in manual practice.
However, our experience says that automation will provide greater results in the future.
'The key benefit of automation is that you speed up the delivery of new features and fixes. For example, we can launch a few testing scenarios at a time or start one scenario on different operational systems, browsers and devices. We also minimize he human factor - no more risks to miss any bug or make mistakes in data processing and analysis.'
Alexander Lukashev
QA specialist at Silk Data
In addition, automation testing leads to lower costs of software development and maintenance.
'Test automation relieves QA specialists from routine tasks, freeing them to focus on other aspects like user research-based approaches. As a result, you get much more confidence about the quality of your final product.'
Alexander Lukashev
QA specialist at Silk Data
At the same time, applying to automation requires vast expertise of QA specialists, so it’d be better to ask professionals for help.
Conclusion
In today’s competitive digital landscape, software testing is no longer optional - it’s a cornerstone of product success .
Businesses that prioritize rigorous testing gain a critical edge, ensuring reliability, security, and better user satisfaction . From unit tests (isolating bugs early) to acceptance tests (validating real-world readiness), each level plays a vital role in quality assurance, while automation becomes an industry game-changer.
Moreover, as industries like healthcare, finance, and retail adopt cutting-edge technologies, testing will grow even more sophisticated - blending automation, AI-driven analytics, and real-time monitoring to deliver flawless user experiences.
So, to succeed in this practice you should build your own skilled testing team or apply to professionals. Silk Data has mastered software testing, implementing the best practices into its projects. For example, you can look at our mobile payment apps, like SQ1Flex, wearonize, SwatchPAY!, where we developed detailed test scenarios for financial applications and conducted in-depth testing of payment system integrations, ensuring compliance with high standards of security and reliability in the financial sector.
Or you may see how we developed and implemented a testing strategy for Waste Removal Calendar environmental application identifying and documenting data synchronization issues, ensuring app’s stability along with the accuracy and reliability of the information provided.
And remember - in a world where 50% of users abandon products after one bad experience, rigorous testing isn’t just best practice - it’s business survival.
Our Solutions
We work in various directions, providing a vast range of IT and AI services. Moreover, working on any task, we’re able to provide you with products of different complexity and elaboration, including proof of concept, minimum viable product, or full product development.